Introduction:
Hearing loss is a prevalent condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Fortunately, the advent of modern technology has provided a remarkable solution: hearing aids. These small electronic devices have revolutionized the way people with hearing loss perceive the world around them. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating realm of hearing aids, exploring their various types, features, benefits, and important factors to consider. By the end, you will be equipped with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about these remarkable devices.
I. Understanding Hearing Loss:
Before delving into the intricacies of hearing aids, it is crucial to grasp the nature of hearing loss. Hearing loss can be classified into three types: conductive, sensorineural, and mixed. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear due to issues in the ear canal, eardrum, or middle ear. Sensorineural hearing loss, on the other hand, stems from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. Mixed hearing loss combines elements of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
II. What are Hearing Aids?
Hearing aids are sophisticated electronic devices designed to amplify sound and improve the overall hearing experience for individuals with hearing loss. They consist of several components, including a microphone, amplifier, speaker, and battery. The microphone captures external sounds, which are then processed and amplified by the amplifier. The amplified sounds are then delivered to the wearer’s ears through the speaker.
III. Types of Hearing Aids:
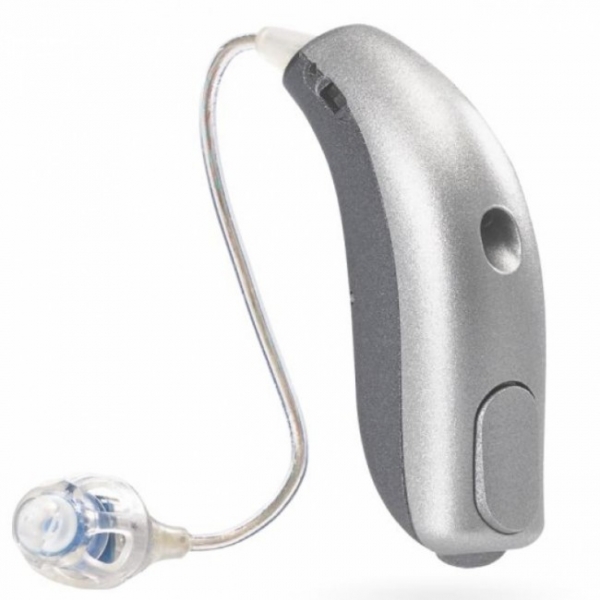
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids: Positioned behind the ear, these devices are connected to a custom earmold or an earpiece that fits inside the ear. BTE hearing aids are suitable for individuals with mild to profound hearing loss and provide robust amplification and diverse features.
- In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids: Custom-made to fit within the outer portion of the ear, ITE hearing aids are more visible than BTE hearing aids but offer greater ease of use and accessibility.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) and Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) Hearing Aids: Similar to BTE devices, RIC and RITE hearing aids position the receiver or speaker inside the ear canal. This design provides a more natural sound perception and reduces the sensation of being “plugged up.”
- Invisible-in-Canal (IIC) and Completely-in-Canal (CIC) Hearing Aids: Custom-made and fitting entirely inside the ear canal, IIC and CIC hearing aids are virtually invisible. These discreet options are suitable for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
IV. Features and Advancements:
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP): Modern hearing aids utilize DSP technology to provide superior sound quality and improved noise reduction, allowing users to focus on speech and important sounds.
- Directional Microphones: Directional microphones assist users in focusing on sounds originating from specific directions, thereby enhancing speech understanding in noisy environments.
- Connectivity: Many hearing aids now offer wireless connectivity, enabling users to stream audio directly from smartphones, televisions, and other devices. This feature enhances the listening experience and accessibility.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Traditional hearing aids require frequent battery replacement, but rechargeable models eliminate the need for constant changes, offering convenience and eco-friendliness.
V. Benefits of Hearing Aids:
- Improved Communication: Hearing aids enhance speech understanding and facilitate effective communication in both quiet and noisy environments.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By improving hearing capabilities, hearing aids contribute to a better quality of life, enabling individuals to fully engage in social activities, work, and relationships.
- Cognitive Benefits: Studies have indicated that addressing hearing loss with hearing aids can positively impact cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
- Emotional Well-being: Hearing aids reduce feelings of isolation, frustration, and depression often associated with hearing loss, promoting emotional well-being and mental health.
VI. Considerations When Choosing Hearing Aids:
- Degree and Type of Hearing Loss: The severity and type of hearing loss are vital in determining the most suitable hearing aid option.
- Lifestyle and Needs: Consider daily activities, environment, and specific communication needs to select features and designs that align with your lifestyle.
- Professional Guidance: Consult with an audiologist or hearing care professional for a comprehensive evaluation, personalized recommendations, and assistance with fitting and adjustment of hearing aids.
- Cost and Insurance Coverage: Hearing aids vary in cost, so it is important to understand your budget and explore potential insurance coverage or financial assistance programs.
Conclusion:
Hearing aids have transformed the lives of countless individuals with hearing loss, reconnecting them with the world of sounds and restoring a sense of normalcy. With their diverse types, advanced features, and numerous benefits, hearing aids offer personalized and tailored solutions for people with varying degrees and types of hearing loss. By embracing the power of modern technology and seeking professional guidance, individuals can experience the joys of hearing and enjoy a more fulfilling life.



